INVIEW Transcriptome Isoform Discover
Isoform sequencing with PacBio’s long-read technology to precisely identify new splicing variants
INVIEW Transcriptome Isoform Discover is a sample-to-data solution which employs remarkably long read lengths to span full-length cDNA. Based on an enhanced ISO-SEQ® protocol, originally developed by Pacific Biosciences, the unique approach enables in-depth profiling of isoform diversity without the need for fragmentation or post-sequencing assembly.
Novel alternatively spliced variants and previously unannotated genes that are difficult or impossible to uncover using short sequencing reads can now be identified.
Applications for INVIEW Transcriptome Isoform Discover
- Discovery of novel genes, novel splice variants and isoforms
- Analysis of alternative promoters, alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation events
- Improving genome annotation of eukaryotic organisms
- Investigating mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation
- Gaining clear insights into protein functional diversity
- Regulation and misregulation of pre-mRNA alternative splicing in cancer and other diseases
Highlights INVIEW Transcriptome Isoform Discover
- Next-generation sequencing (NGS) of fragments up to 10K to generate high-quality, full-length transcripts without any assembly
- Single-molecule sequencing with one read per transcript
- Unbiased sequencing of difficult genomic regions like GC-rich areas and tandem repeats
Full-service package offered by INVIEW Transcriptome Isoform Discover
- Optimized workflows for construction of complex full-length cDNA libraries
- Enhanced protocols based on PacBio’s ISO-SEQ® approach
- Next-generation sequencing of full-length, single-molecule cDNA (four size selections: 1 kb - 2 kb / 2 kb - 3 kb / 3 kb - 5 kb / 5 kb - 10 kb)
- Sequencing using PacBio’s ultra-long read SMRT® technology
- Additional data packages for increased sequencing depth
- Optimized BioIT for unambiguous identification of transcript variants
- Comprehensive GATC Data Report including raw data
- Applicable to any organism with alternatively spliced genes
Starting Material
- Total RNA (3 µg) with a concentration of 300 ng/µL
Specifications
Batch size
- Any number of samples, starting from one sample
Technology
- SMRT® technology on a Pacific Biosciences RS II
Bioinformatics analysis
- Generation of consensus sequences
- Identification of full-length reads
- Detection and removal of artificial chimeras
- Isoform-level clustering
- Consensus polishing
Generation of consensus sequences
- Identification of full-length reads
- Detection and removal of artificial chimeras
- Isoform-level clustering
- Consensus polishing
Deliverables
- Raw data (fastq, bas.h5, metadata.xml)
- Sorted "Reads of Insert" (fastq, fasta)
- Consensus sequence of isoforms (fastq, fasta)
- Comprehensive Data Analysis Report (pdf)
Delivery time
- 30 days for up to 4 samples, more samples on request
Please note that only S1-classified material is accepted for RNA isolation ordered online. More information about the current rules for classifying biological material can be found here.
Background Information
Alternative RNA splicing is a well-known phenomenon, but a complete catalogue of isoforms that account for variability in the human transcriptome is still lacking. Significant progress has been made in developing methods to study variability of the transcriptome to provide a full picture of the transcriptome in the near future.
INVIEW Transcriptome Isoform Discover is our Sequencing Solution for in-depth analysis of transcript isoform diversity. The product combines preparation of complex full length cDNA libraries, sequencing on the PacBio platform RS II and comprehensive BioIT analysis to enable the systematic characterization of alternative splicing, alternative promoters and alternative polyadenylation events in eukaryotic cells. With reads that span the entire transcript length, complicated post-sequencing assembly becomes unnecessary. The product instead relies on analysis of single, full-length molecules to provide unambiguous identification of novel gene variants with biological relevance.
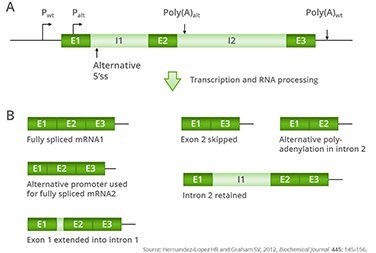
Possible products of alternative splicing of a hypothetical gene
(A) Structure of a three-exon, two-intron gene. Exons are illustrated in dark blue and introns in light blue. Two alternative promoters, one upstream of the coding region (Pwt) and one in the first exon (Palt), are shown as black arrows. Two alternative polyadenylation sites are shown as blue downward arrows and indicated as poly(A)wt for the most frequently used polyadenylation site and poly(A)alt for an alternative polyadenylation site in intron 2.
(B) Some examples of possible mRNAs that could arise from transcription using alternative promoters and using alternative splicing and polyadenylation. The 3′-untranslated region is shown as a black line.