Absorbance (optical Density)
The concentration of oligonucleotide in a sample is measured by its absorbance at 260 nm according to the Beer-Lambert law.
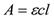
Where A is the absorbance (optical density or OD), ε is the molar extinction coefficient, c is the concentration, and l is the pathlength.
Update
New formula to calculate the concentration of an oligo
Eurofins updated the formula used to determine the oligonucleotide concentration to support you with more accurate values for your applications. Concentration is calculated based on the absorbance, which is a measure of optical density (OD), and the molar extinction coefficient.
The former calculation used a unique constant for each base in the sequence multiplied by the number of each respective bases. The new calculation considers adjacent bases in the formula. Most customers will not be able to tell a difference between concentration calculated one way versus the other. Typically, the values are within 1-2% of each other and also within normal variation of absorbance measurement equipment.
More on the relationship between OD and Extinction Coefficent
The relationship between the amount of substance, measured OD260 and molar extinction coefficient at 260 nm (ε260) is given as:
nmol = OD260 x 106 / ε260
The molar extinction coefficient is a unique constant of each oligonucleotide determined by the nucleotide composition.
The ε260 of the oligonucleotide is calculated as the sum of all ε260 values of the nucleotides composing the sequence.
What changed?
The formula that Eurofins previously used to calculate the amount of substance is:
nmol = OD x 100 / (1.54 x nA + 0.75 x nC + 1.17 x nG + 0.92 x nT)
(n = number of respective nucleotides)
The new formula is based on the nearest-neighbor method and takes into account the sequence specific effects.
nmol = OD x 106 / ε260
Overall, the new formula is more accurate because it takes into account that certain bases couple better than others, which increases their absorbance. Accounting for the adjacent bases in the absorbance measurement is informally referred to as “nearest-neighbor” method. Nearest-neighbor and individual-bases extinction coefficients are used in the nearest-neighbors formula when calculating the final, total extinction coefficient of an oligonucleotide:
Impact of Change?
The impact is small. Most customers will not notice a difference in the concentration values reported on their datasheet. Typically, the values are within 1-2% of each other and also within normal variation of absorbance measurement equipment.
Oligo Analysis & Plotting Tool